Rapid technology breakthroughs and new market entrants are redefining every element of the Telecom business, making digital disruption the new standard. This is happening across every aspect of network infrastructure, content delivery, and access channels.
With the introduction of technologies such as 5G and IoT, the Telecom sector is shifting towards AI-enabled solutions, efficient network management, and infrastructure sharing. But that’s just the tip of the iceberg.
Let’s have a closer look at the key trends that will determine the speed of Telecom business growth in 2024.
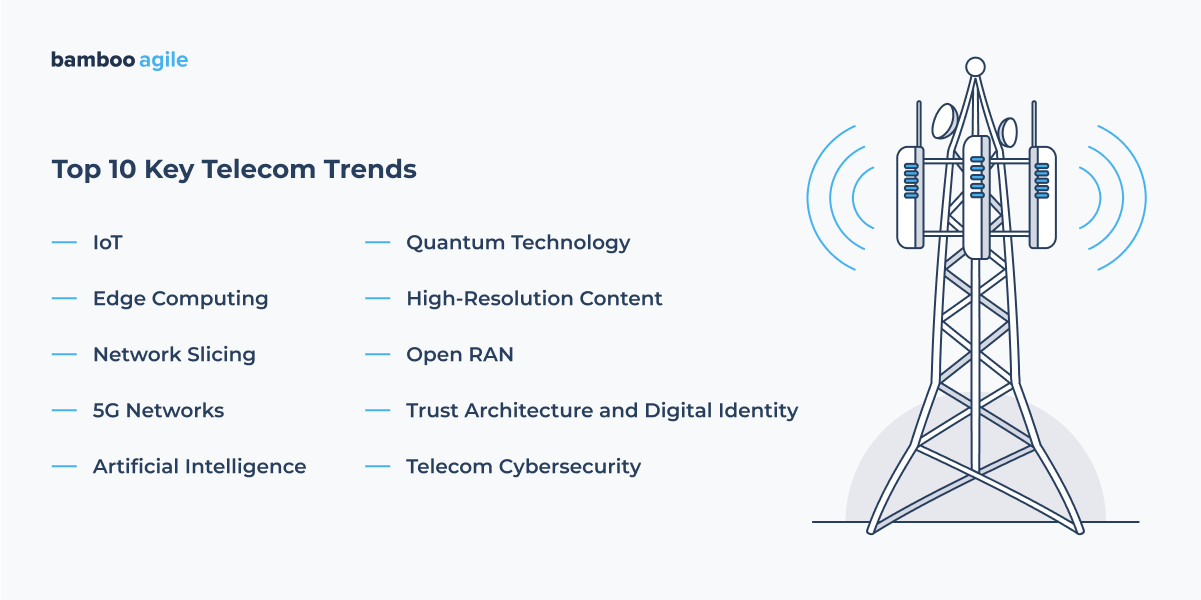
Telecom Industry: Top 10 Key Trends
IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is one of the top trends in telecommunication industry shaping the environment with its disruptive potential. Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) technologies, such as LoRaWAN and NB-IoT, are critical in enabling the mainstream adoption of IoT applications.
LPWAN improves device power consumption, system capacity, and spectrum efficiency. LoRaWAN has grown notably, especially in Europe. Here, its networks have grown by an impressive 66% over the past three years. LoRa allows devices to communicate within a range of 5 to 10 kilometres. It is ideal for a variety of use cases and can be used in both urban and rural locations.
However, it should be noted that LoRaWAN demands an intelligent network infrastructure to function well. That’s because things like physical barriers can impede data transmission. Nonetheless, LoRaWAN remains appealing for urban areas because it runs without a licence. So it provides cost advantages for communications service providers (CSPs) and device makers alike.
Another notable LPWAN technology is the Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT). It facilitates IoT adoption through mechanical design advances and enhanced internet security. NB-IoT is utilised for ultra-low-power, long-range industrial, scientific, and medical sub-GHz spectrum applications.
As IoT connectivity and applications expand, so does the number of IoT devices. And stable network infrastructure will be absolutely necessary for said devices to function and integrate correctly. All this leads to IoT’s rapid expansion and adoption across industries.
Edge Computing
Edge computing is when computer workloads spread across remote data centres. This makes latencies decrease, bandwidth improve, and organisations gain greater control over their data.
The technology also enables real-time data processing, which opens up new use cases in various industries. These industries include remote healthcare treatment, remote mining operations management, and sustainability solutions such as smart grids that optimise energy consumption.
A recent McKinsey survey of 75 Telecom executives from North America and Western Europe revealed a high level of interest in various kinds of edge computing use cases.
- According to the survey results, the majority of Telcos are experimenting with edge computing.
- A quarter have actually deployed it or are actively planning to scale it.
- More than half of the executives questioned (55%) stated their top priority is to improve network efficiency and performance.
- Others mentioned allowing new use cases for companies (21%) or customers (18%).
As Telcos adopt edge computing, they will incur growing costs from energy usage, network maintenance, and investments in changing the network backhaul and backbone. The move towards edge computing also necessitates skills in network and system development to work on data strategy and architecture.
Some of the necessary expertise includes:
- Network engineering, allowing the setup and integration of equipment, software, and systems.
- Network inventiveness, to improve the efficiency of systems.
- Maintenance of networks, to fix breaks and manage emergencies.
- Database administration, to manage data storage, distribution, and analysis.
- Security, to reduce fraud, monitor risk, and handle compliance.
Network Slicing
Network slicing is the ability to build virtual networks on top of a single physical infrastructure.
Imagine a physical roadway with separate lanes for various types of cars. Network slicing works similarly, allowing the establishment of several virtual networks. Each network has specific characteristics to meet the unique needs of different applications and user groups. This method promotes flexibility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness for both operators and end users.
The importance of network slicing arises from its capacity to address several major issues confronting the Telecommunications industry.
For starters, it meets the growing demand for bandwidth and a wide range of network activities. With the rise of data-intensive applications, traditional networks are struggling to keep pace. Network slicing enables operators to deploy resources more efficiently. It ensures that each virtual network has the appropriate bandwidth, latency, and security features to meet its intended function.
Second, network slicing enables operators to generate whole new revenue sources. Operators can differentiate their services by establishing customised network slices geared to specific businesses or use cases. This opens up opportunities for collaboration with other industries, resulting in a win-win situation for both the operator and the enterprise customer.
Furthermore, network slicing enables the creation and deployment of novel applications. With the flexibility to adapt network resources to specific requirements, developers can construct apps that require low latency or high bandwidth and still remain confident that their performance will not be compromised by other network traffic. This supports an innovation environment, resulting in the birth of totally new types of applications and services.
However, it is important to recognise that network slicing is still in its early phases. Several hurdles must be overcome for it to fulfil its potential. Standardisation of equipment from different suppliers is crucial for ensuring interoperability and smooth operation of network slices. Furthermore, strong security measures must be developed to ensure the isolation and protection of each virtual network.
5G Networks
5G is at the forefront of Telecom industry trends in 2024. It has the potential to generate massive economic and societal advantages. Currently, at least 113 operators offer commercial 5G services. This global expansion demonstrates the industry’s commitment to investing in 5G networks. That, in turn, will provide more bandwidth, higher user density, and reduced latency worldwide.
It’s projected to be one of the most lucrative technologies for Telecom. According to IHS Markit, the global 5G value chain is expected to create $3.8 trillion in economic activity and provide 22.8 million new jobs by 2035.
The whole potential of 5G applications has yet to be realised. However, their impact on numerous industries is already becoming clear. From digital manufacturing solutions and multichannel retail experiences to medical improvements and smarter classrooms, 5G is poised to transform sectors and drive innovation everywhere.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) continues to impact businesses around the world. The Telecom sector is no exception. Telecom service providers are proactively using AI and intelligent automation to improve client experiences, and increase operational efficiencies.
Machine learning (ML) technologies are also being used to automate procedures, speed up decision-making, and enhance overall service quality. In 2024 AI solutions in Telecom will continue to improve, achieving increased network and process automation for everything from site setup to service provisioning.
AI’s powerful analytical skills are allowing operators to design highly intelligent networks, forecast network traffic, optimise performance, and proactively address network problems.
The first iteration of the app employs OpenAI’s ChatGPT capabilities. But the developers intend to make it interoperable with other generative tools.
The company collaborated with Microsoft to make Ask AT&T safe and secure for both employees and corporate data. It runs in an AT&T-specific Azure tenant that has been pressure-tested for leaks.
Out-of-the-box use cases for AT&T include:
- assisting coders and software engineers across the firm to become more productive;
- aiding in translating customer and employee documents from English to other languages;
- simplifying and improving usability.
Among other explored use cases are network optimisation, legacy software code and environment upgrades, improvement of the efficiency of care representatives, and more.
Quantum Technology
Quantum key distribution (QKD) networks enable the secure exchange of cryptographic keys. According to McKinsey, over half of executives are currently using quantum technology. Their aim is to protect customer data, simplify procedures for authenticating users’ IoT devices, protect Telecom infrastructure through encryption, or encrypt network traffic.
At the same time, quantum computing threatens traditional encryption methods by creating new attack vectors. Organisations are already concerned about “harvest now, decrypt later” attacks. This is when hackers grab encrypted data to decrypt it later using quantum computers.
By leveraging quantum technology, Telcos can arm themselves with tools to battle these sophisticated attacks. For example, QKD alerts communication parties if an attacker attempts to gather information from an encrypted transaction.
Advances in quantum technology have the potential to vastly improve processing performance and communication speed. But despite Telco leaders’ enthusiasm, relatively few companies are actively using quantum at scale.
High-Resolution Content
The wide usage of smartphones and reliable internet connections have resulted in greater consumption of high-quality content, be it photos, videos, or music. The problem is, HD content frequently comes with enormous file sizes.
In response to this, Telecommunications technologies help organisations adapt to this weightier stream of media. This includes new media types, such as virtual, augmented, and mixed reality (VR/AR/MR) experiences, as well as cloud-based gaming.
These new content formats also need high-speed data transfer, as well as low latency to be enjoyable. So all of this is prompting companies to focus on building strong, high-capacity communications networks.
Open RAN
A radio access network (RAN) is a type of mobile network which links end-user devices, such as smartphones, to the cloud. This is accomplished by transferring data via radio waves from such devices to RAN transceivers, and then from the transceivers to the core network, which connects to the worldwide internet.
For Telecom network operators, RANs are critical connection points that represent major overall network expenses, perform heavy and complicated processing, and are currently seeing fast increasing demand as more edge and 5G use cases arise for telco customers.
New approaches to RAN can provide Telcos with greater flexibility in their relationships with OEMs. They can also minimise the need for such physical assets as towers, antennas, and cabling. This can result in lower capital and operating costs, quicker implementation of new network services, and increased vendor competition.
These new approaches fall under the umbrella of “xRAN”. It includes open RAN (ORAN), which, when mature, will allow for seamless interoperability among hardware and software from disparate vendors.
Open RAN Advantages
Nowadays ORAN is gaining traction due to various factors.
Traditionally, mobile network operators (MNOs) relied on a single vendor to supply their entire RAN infrastructure of hardware and software components. This “closed” system locked operators into specific vendors, limiting their flexibility in terms of pricing, features, and innovation.
Open RAN disrupts this model by adopting open interfaces. It allows operators to mix and match components from different vendors. This opens up a larger pool of options, fostering competition and potentially leading to lower costs and improved functionality.
In a way, Open RAN fosters a more open and collaborative ecosystem, encouraging innovation from diverse vendors. It also leads to faster development cycles and the regular introduction of new features. So MNOs can tailor their networks to diverse customer demands and niche market segments.
By breaking the reliance on single vendors, Open RAN introduces competition into the RAN equipment market. This can potentially drive down hardware and software costs for MNOs, as well as result in more efficient network deployment and operation. Additionally, the modular nature of Open RAN allows operators to replace individual components instead of entire systems. That means reduced upgrade and maintenance costs.
Open RAN Challenges
While Open RAN offers numerous advantages, security concerns remain a key challenge. Integrating components from various vendors raises concerns about potential vulnerabilities and the need for robust security protocols to ensure network integrity and user data protection.
In addition, Open RAN is a relatively new technology. Its long-term reliability and performance compared to traditional closed systems are still being checked.
Some governments view Open RAN as a strategic tool to diversify their Telecommunications infrastructure and reduce dependence on specific vendors. This can be especially relevant in regions with concerns about vendor dominance or potential security risks associated with certain technology providers.
Open RAN Use Case
Ericsson is going to become one of the trendsetters when it comes to Open RAN implementation. The company is planning to implement a broad variety of Ericsson 5G Open Radio Access Networks services and products to support AT&T’s statewide Open RAN ambitions in the United States.
Essentially, it means Ericsson will develop a 5G network architecture for AT&T. It’s going to be based on cloud-native technologies and Open RAN standardised interfaces, with industrial scale, cost-effectiveness, sustainability, and high performance in mind. Over time, AT&T and Ericsson will evolve this into a cloud-native open network.
Trust Architecture and Digital Identity
Trust architecture is the infrastructure and systems that enable trust in the digital age. It includes the technology, protocols, standards, and practices that allow for secure and dependable online communications. Trust architecture seeks to preserve data, privacy, and identity in a digital context.
A digital identity is a digital image that represents a person, organisation, or gadget. It comprises attributes, credentials, and authentication systems for verifying and establishing trust in online interactions. A strong digital identity is essential for gaining secure access to digital services, conducting financial transactions, and more.
Trust in the digital age is based on several essential pillars.
- Authentication entails ensuring that everyone involved is who they claim to be;
- Authorisation that involves granting appropriate access permissions and rights depending on identity and circumstance;
- Data protection as the process of encrypting and securely storing sensitive information;
- Privacy means respecting people’s rights to manage their personal data;
- Compliance means adhering to the legal and regulatory obligations governing data and identity management.
Telcos can validate identities based on both personal information and physical or online conduct. This is done with the help of the following datasets:
- Know-Your-Customer (KYC) information. As of 2023, the majority of national governments (approximately 160) require mandatory SIM-card registration. Slightly under 20 of these additionally require biometrics, such as fingerprints or a facial scan. Eight more nations are in the process of enacting similar regulations.
- SIM card activities. Telcos collect information on any changes to the related device or network for a SIM.
- Location info. Telcos can obtain both a user’s current and past location data.
Mobile Connect’s extensive framework serves as the foundation for Telecoms’ entry into the digital identification market. Established by the GSMA in 2014, Mobile Connect aims to provide a common standard for carriers using digital identity solutions.
Although Mobile Connect has been implemented by over 70 operators worldwide, the collaboration between SK Telecom, KT, and LG Uplus represents the most successful integration of this framework to date.
Telecom Cybersecurity
In 2023, the global market of cybersecurity was estimated to be worth $172.32 billion. It is predicted to expand at a rate of approximately 13.8% per year between 2023 and 2030 to reach $429.97 by the end of the forecast period.
This is due to the rise of current technologies such as cloud computing, Internet of Things, and 5G. But while they might have simplified and automated many industry processes, they have also increased Telecom’s vulnerability to cyberattacks. There are multiple new threats businesses need to consider.
Telecom companies are actively investing in advanced security systems, privacy technology, and compliance processes. They also devote resources to security education for their staff, do regular vulnerability assessments on their systems, and leverage AI and machine learning for real-time threat detection.
Latest App Trends in Telecom

Local Digital and Financial Services Apps
The landscape of the Telecommunications industry is rapidly evolving. One of the most prominent trends is the rise of local digital and financial services apps developed and offered by Telcos. This shift represents a strategic move by Telcos to diversify their revenue streams. It also caters to the growing demand for convenient, accessible, and locally tailored digital services.
Several factors are fueling the development of such apps by Telcos:
- Increased smartphone penetration. The ubiquitous presence of smartphones has created a massive user base for mobile applications. Telcos are well-positioned to leverage this potential. After all, they have an existing customer base and established distribution channels.
- Evolving user needs. Consumers are increasingly seeking convenient and accessible digital solutions for their everyday needs. It includes financial, e-commerce, transportation, and healthcare services. Telcos are well-placed to address these needs by offering localised and integrated solutions.
- Underbanked populations. In many regions, a significant portion of the population remains unbanked or underbanked. Telcos, with their extensive reach, can offer financial inclusion solutions, such as mobile wallets and micro-loans. It promotes financial literacy and economic growth.
How are mobile apps driving the telecom industry?
Download this white paper to learn about the state of the market and the features your app can benefit from.

Developing local apps for digital and financial services offers several advantages for Telcos. Among them are diversification of revenue streams, customer retention and engagement, enhanced brand image, and more.
But while promising, this trend also presents some challenges.
Telcos face competition from established players in the finance and technology sectors. It requires them to offer unique value propositions and build strong partnerships. Also, navigating the evolving regulatory landscape for financial services and data privacy is crucial for Telcos venturing into this domain.
Another challenge is that developing and maintaining robust digital platforms requires significant investment and expertise. It’s more important in areas like financial technology, user experience design, and data security.
Orange’s “Max it” super app is built for Africa and Middle Eastern countries. Its aim is to be a mobile services portal that streamlines the digital experience and makes it easier to complete daily tasks for all users, regardless of whether they are Orange subscribers or not.
The application combines three main services: mobile and fixed lines management, Orange Money functionality (money transfers, payments, bank transfers, credit, and savings), and an e-Commerce platform with digital content. This content includes games, music, news, TV, videos, and more. The application is available on App Store and Google Play and supports different languages.
The collaboration between Microsoft and Vodafone similarly focuses on digital and financial services. These two companies have signed a deal to develop this solution for SMEs across Europe and Africa. The platform is going to be built on Microsoft’s customer-focused AI services, based on OpenAI technology. Vodafone will give access to its managed IoT connectivity platform.
Augmented Reality Apps
The Telecom industry is continuously on the lookout for innovative ways to enhance customer experiences, optimise operations, and unlock new revenue streams. In this context, augmented reality (AR) is emerging as a game changer. It offers significant potential to revolutionise various aspects of the industry.
Unlike virtual reality (VR) which creates entirely immersive digital environments, AR overlays digital elements onto the real world when viewed through a smartphone camera or smart glasses. This unique ability allows for a blend of physical and digital experiences.
Among the key ways AR is being utilised in the Telecom industry are:
- Enhanced customer support. AR can revolutionise customer service by enabling remote visual assistance. Imagine a technician wearing AR glasses and receiving real-time instructions or even guidance from a remote expert while troubleshooting equipment on-site. This can expedite problem resolution, reduce the need for physical visits, and improve customer satisfaction.
- Interactive training and onboarding. AR can create interactive training modules for new employees. It will allow them to learn complex procedures by visualising equipment, processes, and safety protocols in an augmented environment. This can accelerate learning, improve knowledge retention, and reduce the need for traditional classroom training.
- Improved field operations and maintenance. AR can empower field technicians with real-time information overlaid on their field of view. This can include equipment schemas, repair instructions, location data, and even 3D visualisations of internal components. This can potentially facilitate efficient troubleshooting, repairs, and maintenance tasks.
- Virtual showrooms and personalised retail experiences. AR can create virtual showrooms where customers can explore and interact with products in a simulated environment, regardless of their physical location. This can be particularly valuable for showcasing new devices or plans. This can offer a personalised and interactive shopping experience.
One of the great examples of AR applications is Vodafone’s AR app for Audi customers. The solution allows the users of the Audi charging hub in Nuremberg to get information about the hub’s services, offers, and functions. Among them are workstations, a bookable meeting room, a terrace, a lounge area and more. The application also acts like a navigator and makes finding the way across the hub easier.
During the Major League Baseball (MLB) All-Star Game and Home Run Derby, T-Mobile has been the event’s official 5G partner. Their tech made it possible for users to overlay 3D graphics onto the field of play. It showed the ball distance, launch angle, interactive strike zones, and more.
And we can’t help but mention the McGraw Hill AR application for K-12 learning. After the update, the application offered expanded subject offerings. This included a new collaborative feature to foster group learning, such as interactive activities to help engage students in new ways. Now the application has Math and Social Studies lessons where students can use AR to visualise various tasks. The developers of the application are planning to expand that functionality even more in the future.
Mobile Security Services
The ever-growing reliance on smartphones for personal and professional tasks has heightened concerns about mobile security. This has paved the way for a significant new trend in the Telecommunications industry: mobile security services. Telecom operators are increasingly offering a range of services to protect their customers’ devices and data, presenting a win-win situation for both parties.
Several factors are fueling the rise of mobile security services:
- Escalating cyber threats. Cyber threats targeting mobile devices are becoming more numerous and sophisticated by the day. These include malware, phishing scams, data breaches, and identity theft. All this is prompting users to seek robust security solutions.
- Increased data sensitivity. Smartphones become archives for personal and financial information. Due to that, the potential consequences of data breaches become more severe. This drives the demand for comprehensive security measures.
- Regulatory landscape. Stringent data privacy regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) are raising the bar for data security. It pushes Telecom operators to offer compliant security solutions.
- Growth of mobile payments. Mobile wallets and contactless payment methods have become an everyday thing. The widespread adoption of such tech necessitates robust security protocols to safeguard financial transactions.
Telecom operators are offering a diverse range of services for mobile security. They include mobile antivirus and anti-malware solutions, web filtering, secure data backup and encryption, lost and stolen device management, identity theft protection, and more.
The adoption of such services presents both Telecom operators and users with several key benefits. By offering extensive security solutions, Telecom operators demonstrate their commitment to customer data privacy and security. Mobile security services also represent a new revenue stream for Telecom operators. It allows them to diversify their service offerings and generate additional income.
What’s more, enhanced security features can significantly reduce churn rate. It happens by mitigating customer concerns about data security and device protection. Offering robust security solutions strengthens a Telecom operator’s brand image as a responsible and trustworthy provider, attracting new customers.
The example that we can mention here is Deutsche Telekom’s Appvisory Secure App Check services. They use AI to boost mobile device security against cyberattacks. The service identifies weaknesses before and after the installation of the application. It helps businesses meet data protection regulations and reduce security risks.
Telecom Industry: a Business Resilience Boost
Telcos exist in a rapid and highly competitive market. It is characterised by technical advancements, regulatory changes, and changing client needs. To prosper in such circumstances, people must be able to defend themselves against real world threats. These threats include external pressures, social shocks, and unexpected events.
In simple terms, Telco businesses must demonstrate resilience by implementing special countermeasures. Ones that will allow them to adapt to change while maintaining service continuity and financial stability. Natural disasters, equipment failures, and cyber threats can all be mitigated thanks to some of the following measures.
Supply Chain Planning, Inventory and Demand Management
Supply chain planning is the coordination and integration of all operations, processes, and stakeholders. It seeks to optimise the entire Telecom supply chain by synchronising and streamlining activities. It’s made to improve efficiency, visibility, and responsiveness with things like forecasting, renewal planning, and stock level optimisation.
Integrating supply chain management systems enables Telecom firms to achieve operational excellence, reduce time to market, optimise costs, improve the customer experience, and capitalise on technological improvements. It also helps improve inventory management and demand fulfilment.
End-to-End Supply Chain Visibility
Most Telecom operators lack real-time visibility into the whole value chain. They also struggle to identify bottlenecks. Slow organisational reactivity to changing market dynamics combined with an inability to foresee risk leads to increased volatility in corporate operations.
As a result, it’s crucial to create agility through real-time end-to-end supply chain insight, as well as to have a way of modelling alternative situations and predicting their impact on the company.
Some advantages of deploying methods and technologies for end-to-end supply chain visibility include:
- Enhanced supply chain visibility and risk monitoring;
- Rapid and effective crisis response with incident monitoring and reporting;
- Improved large event responsiveness through crisis response using modelled scenarios;
- Improved operational excellence;
- Lower cost of products sold and improved cash release.
Digital Transformation
According to EY research, 64% of supply chain executives in the United States intend to make larger investments in digital transformation to boost its resilience. The poll identified two main methods: more automation and investments in AI and machine learning.
AI and ML techniques can aid in predictive maintenance. That’s done by detecting potential flaws in equipment before they arise and providing a longer lead time for ordering repairs. The use of connected IoT sensors simplifies the monitoring and control of operational assets and reveals opportunities for improvement. As a result, the technology enables round-the-clock tracking of goods and vehicles.
Using complex analytics, AI modelling, and optimisation algorithms, Telecom supply chain teams can analyse complicated data, evaluate complex scenarios, and make data-driven decisions. And optimising network architecture, resource allocation, and operational processes will naturally result in better customer service, lower costs, greater agility, and increased market competitiveness.
Enterprise asset management
Telecom operators rely on a vast and complex network of assets such as towers, cell sites, fibre optic cable, and network equipment. However, they must continue to invest in infrastructure to compete with other companies and meet customers’ growing demand for data connectivity in the 5G era.
According to the GSMA findings, Telecom operators are likely to invest more than $1 trillion in their networks globally by 2025. To manage all these assets, advanced management capabilities are required.
Telecom firms can use resource management systems to efficiently plan end-to-end asset management processes. This is especially necessary when dealing with many assets from different vendors.
Such software will also provide the necessary amount of data for developing predictive and prescriptive maintenance plans. That can help in avoiding unforeseen network equipment breakdowns, which are detrimental to subscribers and the company’s budget.
That aside, Telecom operators must reconsider their asset strategy to reevaluate their core and non-core assets.
Telecom Market: Value Proposition Changes
Reliable, high-quality coverage is the bedrock of any successful network. Imagine seamless connectivity, uninterrupted calls, and lightning-fast data transmission – that’s the foundation for a truly satisfying customer experience. But the value proposition extends far beyond just connectivity. Today’s savvy customers expect a wide range of tailored services rolled into one convenient package.
Looking ahead, personalisation and top-notch customer care will be the cornerstones of increasing customer satisfaction. Forward-thinking providers are embracing advanced technological solutions to make interactions smooth and effortless. Additionally, data-driven business models are being developed to offer customised plans and flexible payment options. It ensures every customer finds a solution that perfectly fits their needs.
How to Create More Engaging Customer Experience by Following Telecom Industry Trends
Personalised experiences, investments in digital self-service portals, mobile apps, and chatbots are just some of the aspects you should consider as a provider. These can improve the customer service and communication method system while offering customers innovative, practical, and efficient ways to address any obstacles along their purchase and consumer journey.
Don’t forget network technology. While Telecom providers have made significant progress in making network services more trustworthy, the introduction of digital tools has reduced wait times, improved problem resolution, and provided greater control over brand interaction management. At the same time, activities like notifications and personalised updates have contributed to increased trust and stronger connections.
Sustainability Practices
The Telecommunications industry plays a crucial role in the connected world. However, its operations can also have a significant environmental impact. Many Telecom companies are embracing sustainability practices to reduce their environmental footprint and operate more responsibly. Here are some key areas where they’re making a difference.
- Energy efficiency. By constantly evaluating and improving network infrastructure, companies can minimise energy consumption. This can involve using energy-efficient equipment, optimising network traffic flow, and employing cloud computing solutions. Telecom companies are also investing in renewable energy sources to power their data centres and network operations. This helps reduce reliance on traditional, fossil-fuel-based electricity generation.
- Reduced waste. Responsible disposal or recycling of old electronic equipment and batteries is crucial. This prevents hazardous materials from entering landfills and ensures proper resource recovery. Furthermore, companies can significantly reduce paper usage, minimising their environmental impact. This can be done by offering electronic billing options and encouraging online account management,
- Sustainable Infrastructure. Constructing and maintaining data centres and other facilities with environmentally friendly materials and energy-efficient designs can significantly reduce their impact. And exploring and implementing innovative eco-friendly technologies can further reduce energy consumption.
- Collaboration and Transparency. Collaboration between different Telecom companies can accelerate progress towards a greener industry. This allows partners to share best practices and develop sustainable solutions. Regularly publishing sustainability reports and setting clear environmental goals fosters transparency and accountability. It allows stakeholders to track progress and identify areas for further improvement.
By implementing these practices, Telecom companies can contribute to a more sustainable future. This not only benefits the environment but also resonates with environmentally conscious consumers and helps to build a positive brand image.
Summary
Within this vast panorama of modern tech trends, disruptive aspects such as AI, 5G, and groundbreaking networking advancements hold the biggest potential to reshape Telecom’s existing model. And recognising emerging prospects and innovative technologies for early integration into your company’s strategy plan will give you a significant competitive advantage.
Get in touch with Bamboo Agile to create your unique custom telecommunications software solutions and join the fast-paced race for Telecom innovation.