Introduction
Whether your new development project is a simple web application or a high-load web service, backend testing is one of the most important stages in ensuring its quality. Simply speaking, your application – be it an online store, a messenger, a startup and its MVP version, a ticket ordering website, an internal business system, an LMS, or a mobile Healthcare app – won’t function unless its backend works in accordance with its technical requirements and user expectations.
In this article, we will look into what backend testing is, its goals, objects, and types. We’ll also give you tips on how to do backend testing and when, as well as which tools to use. And finally, we’ll take a brief look at backend automation testing.
What Is Backend Testing
Backend testing is a complex of methods and special techniques for testing the databases of web applications and software, determining their level of quality, and avoiding defects or blockings during their operation and interaction.
Backend testing includes: ACID principles, schemas, migrations, CRUD operations, security, and performance.
- ACID principles (Atomicity Consistency Isolation Durability) are a formal set of database characteristics which guarantee the stability of digital transactions. The characteristics are, as the abbreviation suggests, atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability. The databases built using the ACID principles have the ability to quickly recover after errors.
- A database schema is a logical description of the settings and configurations of the whole relational database and its separate parts. Schemas come in different forms: for example, they can be visual graphs or formulas written in the SQL language.
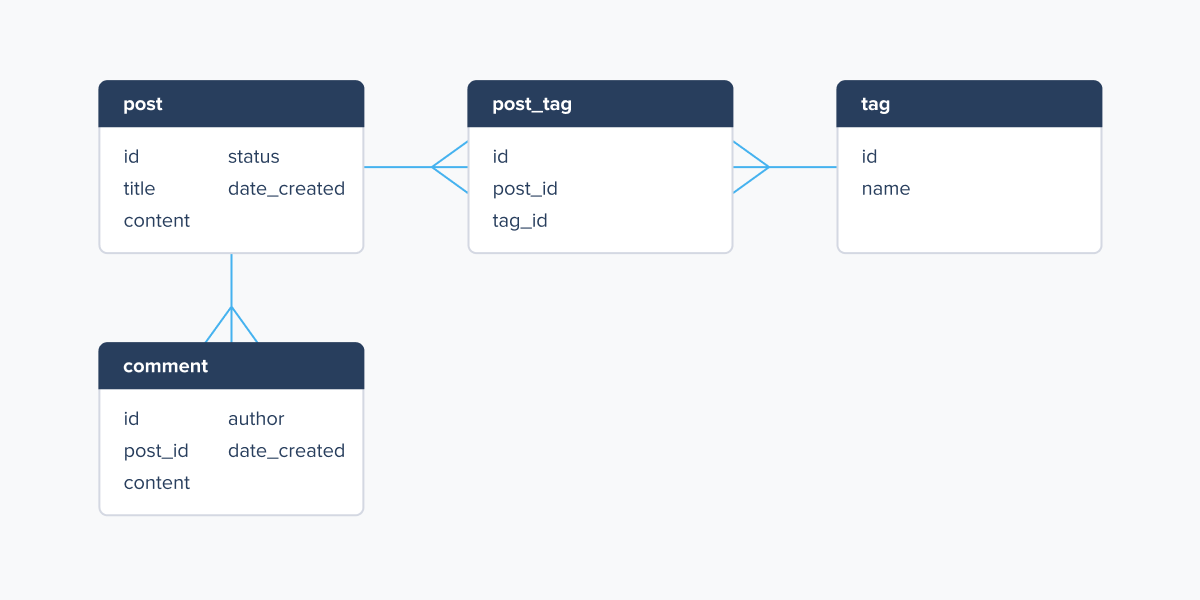
- Database migrations is the process of moving the whole database from an old location to a new one. Say, you were developing your website on a local server, but now that the development has finished, you want to move it to a cloud structure. The process of transferring the database from the local server to the cloud will be what we call database migration.
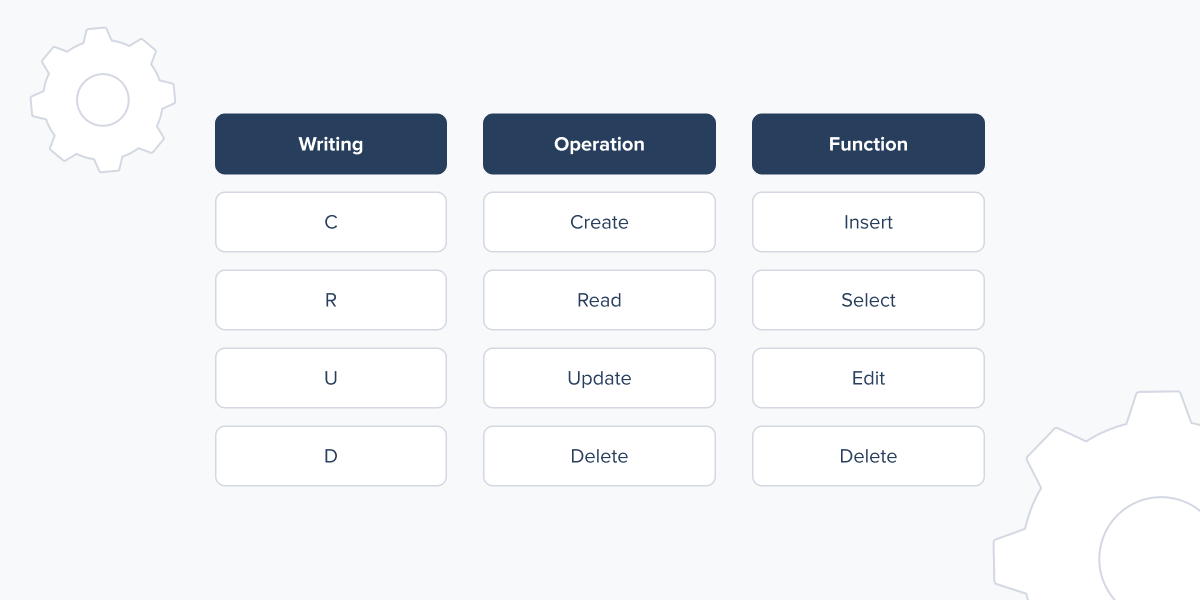
- CRUD operations are the four main operations used in programming databases: CREATE, READ, UPDATE, and DELETE. These help manage databases.
- Security is a certain assortment of measures allowing developers to protect the data stored in a database from third parties (malefactors), as well as from data loss and damage.
- At the same time, performance ensures the stable functioning of the database, correct recovery in case of errors, and uninterrupted work in case of a sharp increase in the volume of data.
By now, it should be apparent that database testing is an integral part of the process of transferring data from the interface to a database. You can be using any kind of database – SQL server, MySQL server, Oracle, etc. – but they must be properly tested to avoid any damage, loss, or change to the data entered.
The Goals of Backend Testing
Backend testing works towards fulfilling a number of aims and requirements. The main ones are as follows:
- Data structure. You must clearly understand that the data entered into certain interface fields must appear in the corresponding fields of the database.
- Following the ACID principles. All transactions in the database must follow the ACID principles.
- Data relevance. The data in the database must be updated in accordance with database normalization requirements, be consistent, and correspond with the data displayed on the user’s monitor.
- Punctuality of business rules. A testing specialist must have the ability to call the necessary components from the complex structure of a database with the help of SQL requests.
The Objects of Backend Testing
Backend testing involves four major object classes that any decent QA engineer must understand:
- Triggers. A trigger is an object that automatically runs a certain event in one of the tables.
- Database (schematic). This includes the design of the database, its structure, entering data into tables, and database normalization.
- Transactions. Transactions are the processes of receiving and processing data. The notion also covers the access to the data stored in each individual table or between them.
- Procedures. These refer to a number of functions aimed at controlling data processing and data access (transactions).
Types of Backend Testing
Not unlike classic web testing, backend testing employs the standard testing types, such as functional and non-functional testing. What makes it stand out is the presence of structural testing. But let’s look at each of them individually.
Structural Database Testing
Essentially, QA engineers must test the multilayer structure of not just the databases, but also of the server side, the integration side. This type of testing is often carried out by experienced specialists that can read code and have the necessary skills in operating specialized software.
Functional Database Testing
The system has to correspond with the functional development requirements and specifications. The main flaw of this testing type in backend testing is that some logic errors and bugs may go overlooked and undocumented.
Non-Functional Database Testing
In addition to functional product requirements, there exist non-functional ones. This type of testing checks the software’s security and performance under high loads. It’s a very important testing stage, because data needs to be protected, while the server side must retain stability and recover with zero data loss as quickly as possible in case of errors.
How to Perform Backend Testing
When to Start Backend Testing
So how does one perform backend testing? To answer this question, we should take a look at the Software Development Life Cycle, and the Software Testing Life Cycle that is directly connected to it.
The following graph shows how SDLC and STLC correlate:
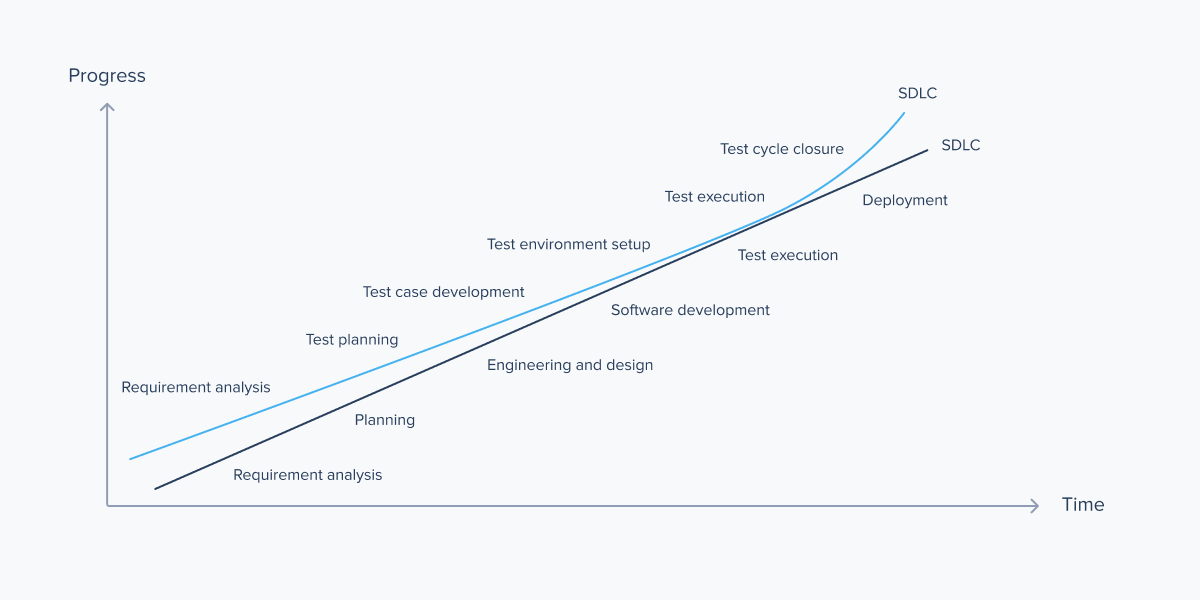
The two cycles converge during the development stage. Therefore, backend testing can be carried out either during the process of backend development (if the cycle is split into backend and frontend development) or when the development of the project has already been completed. In the latter case, the backend is 100% finished and requires additional checkups or needs to be tested after an update – for example, when a modernized version of the software is released. You can read more about application modernization here.
Of course, you can do backend testing of a project at any given point of its existence. Still, it’s better to do it at the start of the development. That way, as the process begins to diversify into its frontend and backend parts, testers can focus their efforts on how to validate the quality of the backend while the frontend is still in development.
Remember, that while backend testing is a complex of measures that can involve various specialists, its global goal is to deliver a high-quality product to the client.
How to Carry Out a Factual Checkup
To carry out a factual checkup, we can use the tool known as CLI (Command Line Interface). We’ll use the following command to connect to MySQL:
mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -u root -p
Where:
- -h refers to the host of the database;
- u is the username;
- p is the password that needs to be typed before pressing Enter.
You can also select a particular database using the command
show databases (which shows all the databases) -> mysql> use ‘database name’.
You can see data tables using the mysql> show tables command and see the structure of these tables using mysql> describe post_estimations.
Moreover, you can use the shell of the operating system itself to get data on the current server load. Connect to it via the web console or via a virtual machine through SSH. Use the system utilities of w, ps, and top to analyze the server load.
- The w utility. The w utility shows how much time has passed since the last launch of the OS, processing power information, and the active connections to the operating system’s shell. Command to use it: w.
- The ps utility. This utility shows the amount of server resources used for every process launched. Command to use it: ps -AH -o pid,pcpu,command.
- The top utility. The top utility allows you to get real-time information about how much of the server’s computational resources are used for a particular process. The best command to use it is: top -c.
Backend Testing Tools
Naturally, if we’re talking about backend testing, we’re also talking about using all kinds of extra tools necessary to carry it out. There are a lot of them, so let’s have a look at the most popular backend testing tools and programs.
Database Schema Testing
SchemaCrawler is a tool for detecting, understanding, and documenting database schemas. You can search for database schema objects using regular expressions and export the schema and its data in an easy-to-read text format. It also allows you to spot potential problems in the architecture.
Stored Procedures Testing
SP Test is a tool for checking stored procedures and streamlining their testing. It lets you test various entry values for the stored procedure.
LINQ adds the ability to make requests in Visual Basic and provides a simple and powerful interface for working with all types of data. Instead of making the database process different kinds of syntax for different kinds of data, the program enters every request as part of the Visual Basic language.
Performance Testing
HammerDB is one of the best programs for load testing the most popular databases in the world. You can load test projects that support the databases of Oracle, SQL Server, IBM Db2, MySQL, MariaDB, and PostgreSQL.
Apache JMeter is another load testing tool. It lets users work with variable and regular expressions, carry out the JSON syntactic analysis, manage cookie files, and a large list of other useful functions. There’s a very easy-to-use plugin for Jenkins, which includes the main load testing scripts that will require only slight modification.
Database Testing
TOAD is a programming tool used to work with management systems for relational databases. In addition to Oracle, it’s supported by Microsoft SQL, as well as other systems and cloud platforms.
MySQL / MariaDB Testing via User Interface
phpMyAdmin is free software created in the PHP programming language. It’s aimed at managing MySQL databases using a web interface. phpMyAdmin is capable of handling a broad spectrum of MySQL and MariaDB operations.
Big Data / Data Link Testing
Data Factory is a specialized API for generating random data. This kind of tool is necessary when developing solutions that require large amounts of different data. The project uses various data sources which can be found in the README files in the src folder of the source code.
Backend Automation Testing
To put it bluntly, the question of backend automation testing is a complex and multilateral one. There are many different opinions on the topic, and all of them are right in their own way – after all, all projects are different and the approaches to backend testing will vary accordingly.
So, we can tackle the idea from several different angles.
Backend Automation Testing as a Frontend Developer
When you’re a frontend developer, you can develop appropriate unit tests for the relevant code.
Backend Automation Testing as a QA Engineer
In turn, the main goal of a QA engineer will be developing tests that reflect real user actions, employing the popular Selenium library, for example.
Backend Automation Testing as a Backend Developer
The classic approach for a backend developer is to write unit / integration tests for the components that are in development. In addition, the backend side may contain various web services which also require testing using SoapUI or other similar software.
Conclusion
Backend testing is a complex of methods and special techniques for testing software databases, built on ACID principles, schemas, migrations, CRUD operations, security, and performance. It is split into functional, non-functional, and structural testing.
Backend testing can be carried out either during the process of backend development (if the cycle is split into backend and frontend development) or when the development of the project has already been completed. Still, it’s recommended to begin it at the start of the development.
If you have any further questions about backend testing and development or are interested in hiring reliable backend software experts, don’t hesitate to contact us for a free consultation.