Fintech Industry Overview
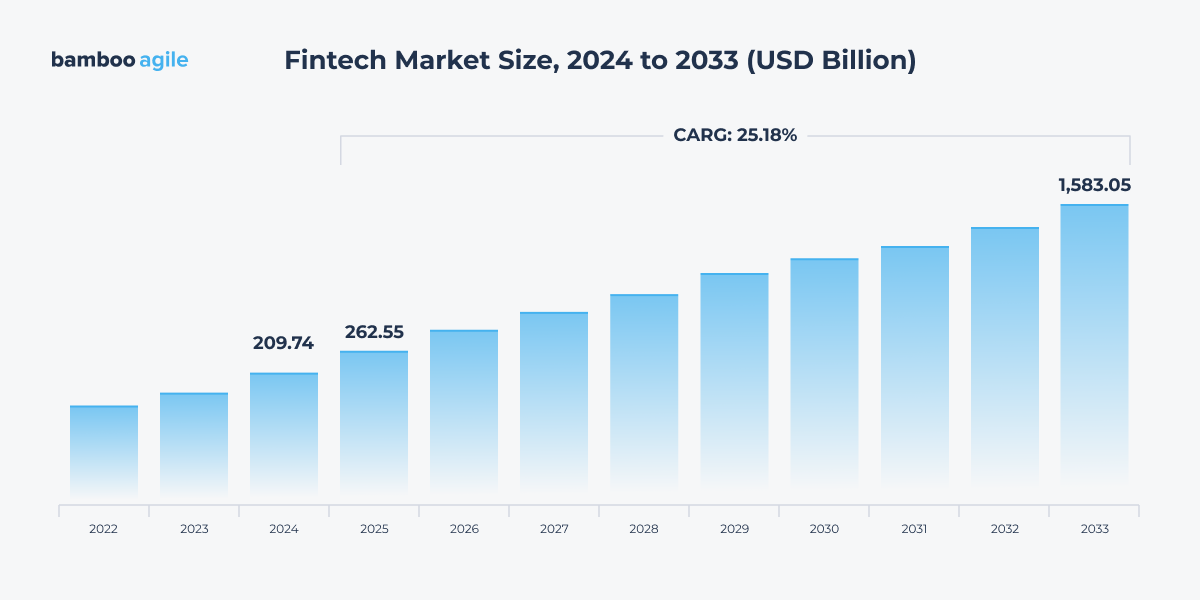
Global digitalization has affected nearly every industry, including fintech. The fintech market was worth $209.74 billion in 2024. Market Data Forecast research predicts that it will reach $1583.05 billion by 2033, with a CAGR of 25,18%.
Fintech is an umbrella term for all financial technologies. Despite its complexity, fintech is gaining traction as a replacement for traditional e-commerce, payments, banking, and wealth management., Both traditional banks and fintech startups are now building innovative mobile apps that are set to reshape the financial industry’s landscape. These developments are expected to generate new value chains across local and international markets, including C2C, B2C, and B2B sectors.
Trends of the Fintech Market
With the technology market expanding by the day, you can use some of the most recent advances to enhance your financial app. Adopting new trends will improve your fintech app development and provide the competitive advantage that any new product demands. Let’s look at the most notable trends affecting the financial market.
Embedded Fintech
According to Forbes predictions, embedded fintech is expected to continue advancing, with a growing focus on solutions tailored to the specific needs of individual sectors. This is possible due to expansion of proprietary data sets and wider adoption of API-driven infrastructure. IndustryARC projects that the global market for FaaS (Function-as-a-Service) will reach $161 billion by 2026.
Instant payouts and financial tools for freelancers, education loans and micro-financing, retirement financial planning and safe digital banking – there is still plenty of room to grow and fintech companies will continue to customize their offers to meet the unique needs of defined sectors.
Artificial Intelligence
While much of the recent buzz around AI has centered on general-use tools like virtual assistants and large language models, financial institutions are beginning to take a more strategic view. Juniper research expects that in 2025 the focus for banks and financial services will shift decisively toward practical, high-impact applications, particularly in fraud prevention and identity verification. As the industry moves beyond the hype, these use cases stand out for their measurable value and urgent need.
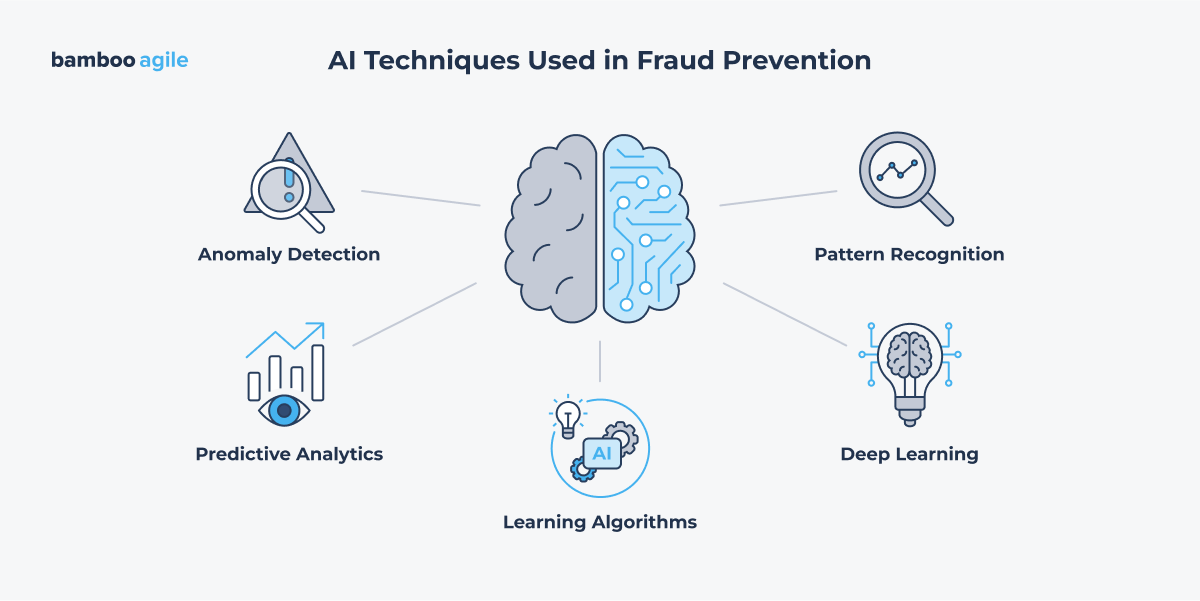
Big Data
Financial organizations must deal with massive amounts of data to effectively predict and identify trends and patterns. Traditional data analytics and management solutions are incapable of handling such massive amounts of data. Collecting information will allow you to gain useful insights that can be used for risk assessments in insurance apps, for example. Another application of Big Data in fintech is accurate fraud detection, which is based on the collection and analysis of usage patterns.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning is unavoidable for banking app development. ML algorithms in the finance industry can assist organisations in making market risk forecasts, algorithmic trading, reducing fraudulent actions, and unlocking potential prospects. Finally, this technology enables robo-advisors, which assist consumers in investment management and educate them on current trends and data security measures.
Blockchain
Many banking professionals believe that digital assets will entirely replace traditional cash in the next few years. Aside from enabling cryptocurrencies, blockchain improves efficiency by eliminating the need for a central intermediary to authorize transactions. As a result, transfers will be performed much more quickly than with regular banks. Blockchain developers can also facilitate transparent and secure transactions thanks to utilizing a distributed database.
Gamification
Gamification in the context of fintech app development refers to the placement of interactive dashboards, the issuance of personal badges, and the engagement of people to fulfil certain activities. Investment applications use this strategy to entice users to start investing even if they don’t have any money, by giving fantasy trading.
Robotic Process Automation
RPA is a technique that uses bots to automate routine and repetitive processes that do not require human intelligence. Data entry or information processing, for example, can be delegated to bots to free up your staff’s time and minimize operating costs.
Biometric Identification
Face and voice recognition, analysis of fingerprints, and more advanced techniques such as palm vein patterns, iris identification, and retinal scanning are all part of biometric authentication.
Moreover, Juniper Research foresees the widespread adoption of behavioral biometrics, a passive and dynamic method of identity verification that continuously tracks a user’s behavior for ongoing authentication. When combined with static biometrics, behavioral one enhances security by creating a multi-modal authentication system that blends physical and behavioral traits. This combination provides unmatched protection without sacrificing user experience.
For example, tracking unique typing and swiping patterns like speed, pressure, and mouse movement enables businesses to detect suspicious activity early, strengthen trust with legitimate users and quickly identify potential threats.
These authentication techniques will considerably improve the security of fintech apps and will be able to completely replace PINs and passwords, which frequently fail.
Smart Contracts
Although smart contracts are built on blockchain, they are much more than that because they use automated clearinghouses and central securities depositories for bond issuance. Smart contracts remove third parties and improve transfer efficiency by increasing speed and lowering expenses.
Types of Fintech Apps
Fintech apps are classified into numerous categories. Let’s go over the most common types.
Payments and Transfers
Traditional payment apps, such as PayPal or Venmo, were designed to help users make mobile payments. Transaction history, currency conversion, and other essential features are must-haves. These applications are becoming more popular as the volume of cross-border money transactions increases.
Wealth and Investment Apps
These fintech apps allow you to buy stocks and ETFs while lounging on your couch at home. They can also recommend investing options based on your preferences.
Cryptocurrency Apps
There is a distinct class of fintech apps that stand out while imitating other financial services apps in terms of features: investing, payments, insurance, wallets, and so on. The only difference is that these apps use cryptocurrencies.
Neobanks
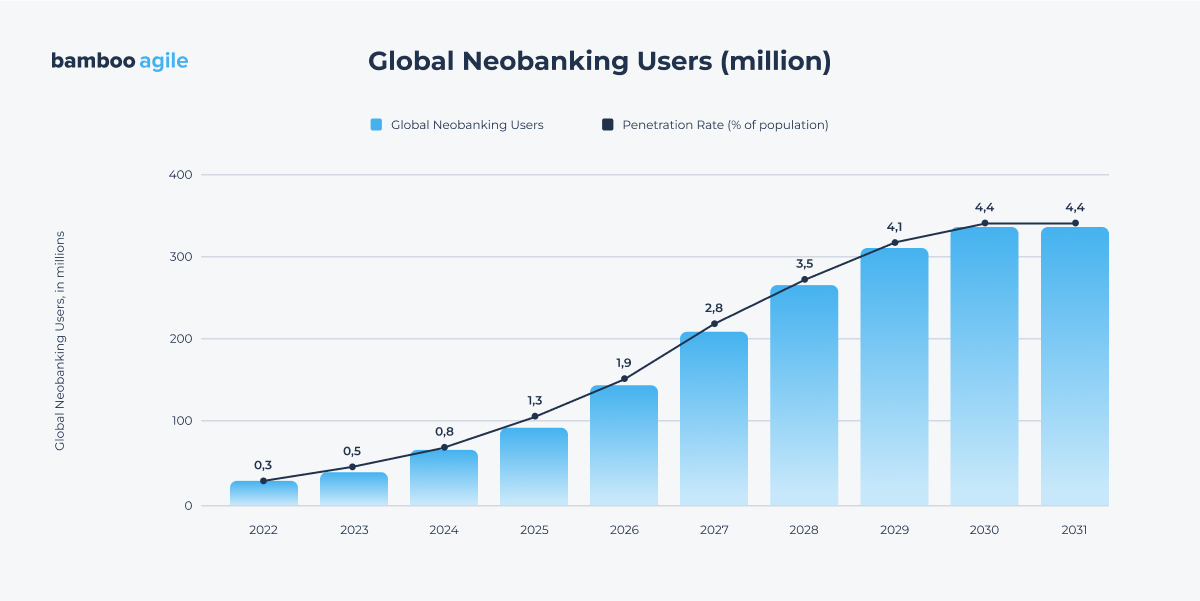
As digital banking continues to grow, neobanks are becoming a go-to option for younger generations, remote workers, and individuals who have been overlooked by traditional financial institutions. By 2028, the number of global neobank users is set to exceed 386 million, reflecting their increasing adoption worldwide.
Personal Finance Apps
Budgeting apps used to dominate app stores just a few years ago. Every personal finance management software is designed to provide the user with a more comprehensive view of their spending and help them with financial planning. These apps typically offer such features as budgeting, expense tracking, bill reminders, and financial goal-setting.
Insurance Apps
Insurance apps make it easier for people to buy, manage, and claim insurance. But customers need to provide plenty of personal information to these apps. As a result, your app should provide a streamlined process through a professional, user-friendly interface. There is an interesting subtype of peer-to-peer insurance services apps that allow users to insure one another.
Lending Apps
Lending platforms connect borrowers and lenders directly, offering faster access to personal, business, or peer-to-peer loans. By using tech to assess creditworthiness and bypass traditional banks, they provide quicker approvals, competitive rates, and broader accessibility.
Banking Apps
Mobile banking apps allow users to manage their bank accounts and conduct financial transactions freely and swiftly. They can also be used to order physical credit cards, exchange currencies, and contact their bank’s support.
Regtech Apps
Regtech (Regulatory Technology) was created to assist financial firms in meeting regulatory compliance requirements. Regtech solutions aid compliance teams in monitoring risks, regulatory changes, and transactions, as well as reducing the frequency of false non-compliance warnings and creating reports.
Consumer Finance
Consumer finance apps help users manage spending, save money, and forecast account balances. They include features like budgeting, bill tracking, investment analysis, payment categorization, and fraud alerts.
Before Developing a Fintech App
Fintech application development necessitates a high level of technological understanding. Here are some things to consider before starting fintech app development.
Choose a Tech Stack
Before you begin fintech app development, you must select a technological stack for the app’s design, development, and testing. However, if you have a limited budget, you must first determine which platforms your target audience prefers between iOS and Android.
You should ideally go for native iOS and Android app development to reach the widest possible user base while maintaining a good level of quality. But this is not always viable, since native development can get quite expensive.
But even if you have a limited development budget, you can go with a cross-platform app to cover both versions. It’s cheaper, but comes at the cost of having perfect platform optimization.
Get a Team or Hire a Fintech App Development Company
Many businesses within the fintech sector outsource app development to save time and money over hiring their own team.
The number and specialty of project team members is determined by the time constraints, technology, and size of the project. Hire Flutter developers, for example, if you want to construct a cross-platform financial app for iOS and Android. The development process will be slightly longer, but you will generate an app for two platforms at the same time.
When selecting a financial software development company, consider the company’s experience, hourly compensation, and quality of professional training. A professional team will always offer you the opportunity to produce a technical specification document that will provide both you and the fintech application development team with a clear project vision.
Define Your Features
The main functionalities you should include in your fintech software differ depending on the type of your financial application. Determine the requirements of your target audience to see which features you should prioritize. You can also build a fintech app based on an existing one and consider how you could improve and simplify it.
The following are the essential components of any fintech app:
- Secure sign-in (combination of voice and face recognition, fingerprint authentication)
- Custom notifications and alerts
- Budgeting and tracking savings
- Money transfers, digital payments, balance checking, and mobile depositing
- Scanning of card numbers and QR codes
Here are also some of the additional features that may give you a great competitive advantage:
- Chatbots driven by artificial intelligence and virtual assistants
- Additional financial services (purchasing tickets, donating money to charity)
- Cashback
If you’ve never worked with a fintech app before, the development company you’ve hired will assist you in defining the minimal functionality.
Create a Compelling UX/UI Design
Design is critical in the creation of fintech apps, second only to security. The interaction with your financial software should be seamless, and the UI should be basic and easy to use.
For example, if you decide to create a banking app, avoid creating big forms that users must fill out to pay bills. Also, provide users with the option of not having to re-enter payment information every time they need to send money.
Still, do make your design distinct so that it draws attention to the main functionality while staying true to your brand image.
Deal With Compliance
There are numerous fintech app security solutions developed to ensure regulatory compliance. You must also follow privacy rules (CCPA, GDPR, LGPD, PIA) to guarantee that all clients’ financial data is secure and inaccessible to unauthorized parties.
The choice of privacy law is determined by the country in which your app will be used. Most countries lack specialised regulatory bodies. You should evaluate all of the criteria specific to the country in which you wish to utilise your app, and you should follow the laws and norms of that country.
Compliance with legal standards is the most important component in achieving success, so approach it very carefully.
A reliable fintech software development services provider should have experts and consultants onboard to make sure your fintech app meets all the necessary standards.
9 Things to Consider When Developing Fintech Apps
Let us walk you through the steps of creating a simple financial app, as well as mention some tools best suited for each of these steps.
1. User Authentication Options
It is extremely important to implement authentication of the highest security level. All payment information is connected to the device, so it should be practically impossible to gain access to data in case of theft.
Firebase is a great architecture tool for this step. Consider it the skeleton on which to hang your app’s muscles and organs. It offers secure user authentication, administration, and crash reporting. Firebase also works with a variety of other Google services to provide a rich user experience.
2. Get Secure Hosting
Hosting is your powerhouse, and you need to keep the powerhouse protected. Cloud Firestore is a secure cloud-hosted database solution for developing applications that are based on Firebase. This product works in tandem with all other Firebase products to provide a unified development and user experience. It features automated scaling, great performance, and streamlines the app development process.
3. Integrate Credit Score Checking
Credit score checking is the process of obtaining a credit score, which is a number that lenders use to assess one’s creditworthiness. The credit score is based on a variety of factors, including payment history, the amount of debt a person has, and the length of their credit history.
Credit score checking is important to track credit history, identify any potential problems, see if a person qualifies for loans or credit cards, and monitor for identity theft.
Here are a couple tools you can use to implement it.
Experian provides a consumer-facing API for retrieving credit score reports. The latter can also be accessed by authorized third parties online. You can generate full credit reports, FICO scores, public data, and conduct credit inquiries using ACS (American Credit Systems).
TransUnion, Equifax, and Experian credit reports are generated through the Universal Credit Services API. UCS combines this information into a single unified credit report file. They also accommodate bulk requests.
4. Access Bank Account
Your app will most likely require access to the user’s bank account to perform transactions.
A great tool for implementing that is Plaid. Plaid integrates apps with financial accounts and is a widely used API in the fintech business. It is highly adaptable and consolidates your users’ data on a single platform, reducing risks and accelerating development.
Yodlee is another financial data aggregator, but it has fewer capabilities than Plaid.
5. Setup a Payment Gateway
A payment gateway is a secure online service that allows merchants to receive payments from customers. It acts as an intermediary between the merchant’s website or app and the customer’s bank, processing payments and transferring funds to the merchant.
There are a number of reasons for businesses to implement a payment gateway:
- It uses the latest security protocols to protect your customers’ sensitive financial information. This helps to ensure that your customers’ data is safe and secure.
- Payment gateways make it easy for your customers to pay for your products or services. They can simply enter their credit card information on your website or app, and the payment will be processed securely.
- It can scale to meet the needs of your business as it grows. This means that you won’t have to worry about your payment processing capabilities as your business expands.
- Payment gateways help you to comply with the latest payment processing regulations. This can help to protect your business from fines and penalties.
Stripe deserves a mention here. This is a worldwide payment processor. Stripe unifies many payment service providers into a single solution, eliminating the need to retain credit card information and comply with PCI certification. Another good thing is that it is compatible with Plaid.
6. Implement Chatbots
ChatBot API automates customer assistance by utilizing Natural Language Processing and machine learning. Because it is powered by machine learning, you can use open-source libraries like Python Scikit to build it to handle more sophisticated jobs like tenant pre-approval processing.
7. Bonus Plugins
If you want to add some extra functionality to your app, you should look into plugins.
Let’s say you wish to incorporate financial management for a business dashboard. Then you should check out the Intuit API, which includes features to display a company’s financial health. The tool comes from the owners of Quickbooks and Mint.
If data visualization is a must for your app, D3 is the framework to use. D3.js is a JavaScript toolkit that allows you to manipulate data to generate visualisations in HTML, SVG, and CSS. This is also the API you’ll need if you wish to include business resource planning and budgeting functionality.
8. Legal Obligations
Remember, we’re dealing with highly sensitive information. This is information that hackers would love to obtain at your expense. So here are a few additional actions you must take to prevent that:
- Understand the legal agreements connected with using these APIs to access consumers’ data.
- Create a policy for data privacy and management.
- Secure insurance coverage to protect yourself in the event of a breach.
- Prepare a catastrophe recovery and business continuity plan.
Your duties extend beyond simply providing a service. Your customers are entrusting you with their life savings. Taking these extra efforts will help to increase their trust in you as well as the dependability of your app.
9. Support
The whole Fintech business relies on confidential data. As a result, you cannot rely on third-party customer support; instead, you must employ consultants to address client inquiries. They should be technically trained to operate under extremely tight safety standards and requirements.
Create a chatbot if you are unable to hire a fintech software development company that is available 24 hours a day, seven days a week. A quality support service will allow customers to build trust in your app and learn about their finances or the bank’s offerings.
Bamboo Agile’s Experience in Fintech App Development
Bamboo Agile has plenty of experience with Fintech. One example of that is e-Wallet. This solution allows users to pay their bills and purchase goods and services in one application.
E-Wallet was built for one of the CIS’s telecommunication services provider, so it processes all the transactions via the local National Information and Settlement System.

Another remarkable project Bamboo Agile took part in is Shape – a modular, web-based Payments-Platform-as-a-Service (PPaaS) that helps payment service providers quickly launch white-label solutions without coding.
Fintech Application Development Cost
The cookie-cutter method rarely works in fintech software development world, and each programme has its own development cost. This is especially true for complicated financial products with various integrations, strong security features, and cutting-edge technology incorporated at multiple levels.
As a result, if you plan to develop a financial app, you should be prepared for continually changing estimates, particularly in the early phases when the scope tends to grow a lot following your arguments on what the app’s MVP version should look like.
However, some t-shirt sizing is still possible for typical fintech apps, taking into account overall market benchmarks: $100,000 – $300,000 for a basic app for iOS and Android, and $800,000 – $1,000,000+ for complex financial products that include various monetization models, complicated features, and third-party integrations.